Many people planning to build a new house are wondering what type of heating should be incorporated into their building plans. They are usually looking for a heating system that will keep the whole family comfortable and works as quietly as possible. And above all, it should be energy and cost-efficient.
Hydronic radiant heating is an underfloor heating system where hot water is passed through a network of small tubed laid under the flooring. This heating system heats up the entire flooring area thus warming up the room without leaving any ‘cool spots’ like traditional fan-driven heating systems.
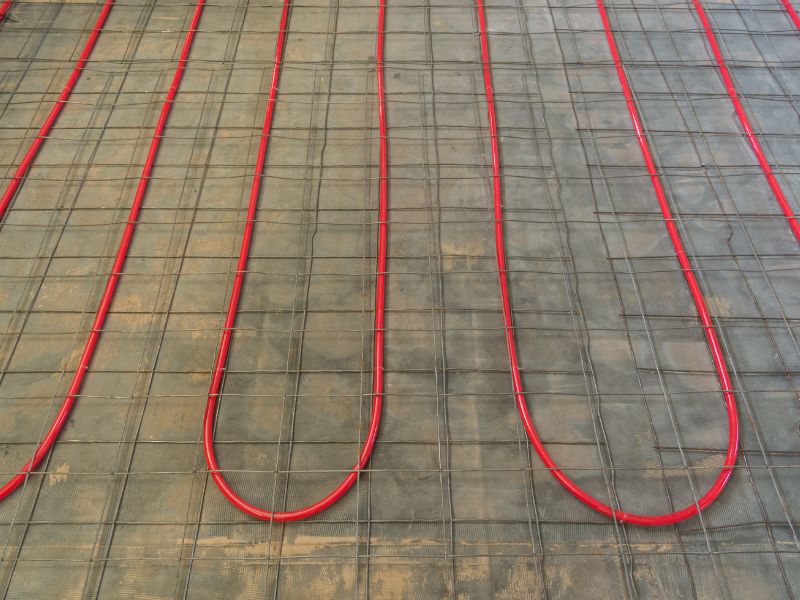
This article will provide you with basic information regarding hydronic heating to help you to determine whether this type of heating is what you need. For your convenience, I provide you with a table indicating the 9 main subjects I’ll discuss in the article. This will allow you to either read the whole article or easily skip to the paragraphs you want to read.
Please note:
Different liquids, other than water, are also being used in modern hydronic heating systems, and apart from floor-heating, wall radiators can be used for radiating. However, in this article, I’ve taken water as the circulating liquid and the floor as the radiating medium, unless otherwise stated.
Diagram of contents
For your convenience, I include this table to make it easy for you to find and use the information you need. I recommend that if you want to find out as much as possible about domestic hydronic heating you read the whole article. But the diagram will help you to find a specific issue without reading everything.
1. Different types of heating
In principle, the transfer of heat can occur in any of three ways: By conduction, convection or radiation.
| Type of heating | Brief description | Example/Application |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Simply put, heat conduction is the movement of heat from one object to another when they are touching each other and they have different temperatures. | A practical example of heat conduction is when you’re standing barefoot on a cold kitchen floor. |
| Convection | Heating by convection occurs when fluids, air or other gases are being circulated from one area to another and in the process transfer heat | Forced-air heating systems are examples of heating by convection. However, air and other gases are poor conductors of heat. |
| Radiation | When heat travels in invisible waves through space it is called heat radiation. The heat waves cannot be blown away by wind and are absorbed by the object that is in the path of the waves. It is a very effective way to transfer heat. | Ideal to use in homes, especially for underfloor heating |
2. Hydronic heating – description and principle involved
2.1 Simple and brief description of what hydronic heating is
Hydronic heating, also known as radiant heating, is a system where water is heated in a boiler and then circulated through a network of tubes beneath the floor of your home.
The heated water is flowing from a boiler to a manifold which is the control and distributing center of the system. This control center is connected to the thermostat(s) and distributes water with the right temperature to the different zones in your home.
The distributing is done by a pump that is constantly pumping newly heated water into the tubing, while cooler water is returned to the boiler to be heated again. It is a closed-loop system.
2.2 The main reasons why hydronic heating is so effective
Forced-air heating systems blow warm air through a duct network to the different rooms in your home. This convection way of distributing heat throughout your home often results in cold spots in the room because of poor circulation.
With a hydronic heating process, however, the whole floor is heated and heat is radiated up from the ground in an even and consistent manner. It produces steady heat throughout the entire room.
The hydronic radiant heat is basically produced in 3 steps:
Step 1: The boiler heats the water.
Your system’s boiler uses conduction to quickly and efficiently heat the water for the system.
Step 2: The pump and manifold distribute the heated water.
The water is pumped to a manifold which is the control and distributing center of the system. This control center is connected to your thermostat(s) and distributes the heated water with the right temperature to the tubes underneath the floor in the different zones in your home.
Step 3: Radiating the room.
The heated water that is pumped in the tubes throughout the house heats the flooring through conduction and then radiates heat into the room. The result is that a consistent temperature radiates not only from the floor surface but also from the solid objects around the room.
3. Flooring options for hydronic radiant heating
Nowadays, hydronic radiant heating systems can be used with literary any type of flooring. Earlier, hot water radiant floor systems were only installed on the concrete slab of a home. New designs and installation techniques now enable homeowners to install hydronic tubing in floor joist systems and below hardwood floors and other floorings like carpets, laminates, and vinyl.
4. Items needed in every hydronic heating system
There are different types of hydronic heating systems available for residential homes. But there are basic things that will always be part of the design, whichever system you choose to install.
The following items are always in some way or another part of your hydronic heating system:
4.1 Boiler
The boiler is the generic name for the apparatus needed to heat the water which will flow through the system. There are different options to consider:
4.1.1 Tank-like heaters
Tank-like heaters are the traditional way of heating the water to be circulated through the system. It is still the most common way in households of providing heated water for the system. It consists of a tank holding the water circulating through the system heated all the time by using electrical elements or gas burners.
4.1.2 Tankless water heaters
Tankless water heaters are also known as on-demand or instant water heaters. Although they have many advantages over traditional tank-style water heaters, they are not necessarily the solution for every home.
Where tank-style water heaters use energy continuously to maintain a hot water supply, tankless heaters only use energy when the system needs hot water. Thus, it is a very energy-efficient system.
Tankless water heaters also don’t need so much space as tank-style boilers. Other benefits include aspects such as the low risk of leaking and a long lifespan. There can also never be a tank explosion.
The high upfront cost is one of the disadvantages of the tankless system. On average, the purchasing and installation of a tankless system cost 3 times more than a tank-type boiler. Another disadvantage is that because there is not a tank with hot water the tankless system cannot provide hot water during a power outage unless it is a tankless heater connected to gas.
4.1.3 Solar Water Heater
Generally, a domestic solar panel will not provide enough heated water for the system, but if it works with your tank-type boiler, it will increase the energy efficiency of the system. With a solar heater, the liquid that runs through tubes inside your water storage tank is heated and the water in the tank is then naturally pre-heated. Thus, less energy is required to bring the water in the tank to the right temperature.
4.1.4 Geothermal Heat Pump
Geothermal heat pumps can also, like a solar panel, preheat the water by using the natural warmth found below the soil. This reduces the energy needed by your boiler.
4.2 Liquid Medium
Traditionally, water has been the liquid medium, and as mentioned earlier in this article, to simplify the reading of this article we always take water as the liquid medium. But you have to be aware of the fact that nowadays you can find systems using other liquids and sometimes using a water and antifreeze mixture.
Glycol, for instance, is a common antifreeze that is added to closed-loop systems. This helps to prevent the water from freezing if the tubing runs through exposed areas. Glycol also increases the water’s boiling point.
4.3 Tubing, pump, and manifold
Plastic tubing like PEX is commonly used and is long-lasting. A pump is needed to circulate the water through the tubing system. But without a manifold that is connected to your thermostat(s), the system cannot function. The heated water is pumped to a plumbing manifold. Because the manifold is connected to your thermostat it can direct the flow of the heated water to where it is needed. The manifold is the center of your whole heating system.
4.4 Heat Exchanger
As mentioned earlier, to simplify the reading we always use the floor as the hydronic heat exchanger in this article. But the floor is not the only possible heat exchanger. Apart from the floor, a radiator or baseboard heater can also be used to transfer heat into the home. Let’s have a look at the different heat exchangers.
| Type of hydronic heat exchanger | Description |
|---|---|
| Underfloor Radiant Loops | Radiant flooring is the most popular as it is relatively easy to add the tubing into the concrete or floor joist system. Underfloor radiation provides consistent and comfortable heating evenly throughout your entire home. |
| Baseboard Heaters/Radiators | Hydronic baseboard units and radiators can be much easier to install for home remodels because they require less tubing below the floor. |
| Walls | Similar to installing a radiant floor, wall radiant panels are available to be placed behind walls, and can heat a broad area. |
5. Pros and cons of a hydronic heating system
Like any system or product, hydronic heating systems have advantages and disadvantages. However, the advantages seem to be more than the cons.
5.1 Pros of hydronic heating systems
The following are the most important pros of a hydronic heating system:
| Advantages/Pros of Hydronic Heating Systems | More information |
|---|---|
| A hydronic heating system offers reduced allergy symptoms. | As hydronic systems don’t use ductwork or blow air into your home, things like dust, germs, viruses, and allergens can’t be blown into your house and trigger allergies. |
| All hydronic heating systems are very quiet. | Hydronic systems don’t use fans in the rooms in your home and thus no fan or blowing noise is audible. |
| It is a good system to include in new constructions. | When hydronic systems are installed no ductwork, vents or registers need to be added. |
| With a hydronic system, it is easy to control separate zones in your home. | By installing multiple thermostats and control valves you can have efficient zone heating. |
| You have a much lower energy consumption with a hydronic system than with any other heating system. | Hydronic heat feels warmer at lower thermostat settings because the heated air doesn’t blow away. Your thermostat can be set at a lower temperature and thus you can save energy. |
| A hydronic heating system is very energy-efficient. | It takes less energy to circulate water than blow hot air so hydronic systems are more energy-efficient than air systems. |
| You have no heat loss with a hydronic heating system. | The heat produced by a hydronic system doesn’t get lost as with forced air systems. |
| A hydronic system doesn’t require any filters. | No filters are needed as hydronic heating systems don’t produce blowing air that needs to be cleaned and filtered. . |
| With a hydronic heating system, you will always have warm and comfortable floors. | Your kitchen and bathroom tiles will never be cold to the touch. You’ll be able to walk comfortably with bare feet in your home. |
| Hydronic heating systems allow design flexibility. | The tubing can be installed in areas with limited airflow, and with zone valves, specific areas can be heated. |
| With hydronic heating, it feels warmer than the actual temperature. | A side-effect is that the radiation of heat in a hydronic system lets you feel comfortable at lower air temperatures than with conventional heating. |
5.2 Cons of hydronic heating systems
Generally, hydronic heating systems are ideal for most domestic situations, but there are some disadvantages to keep in mind.
| Cons of hydronic heating systems | More information |
|---|---|
| Your hydronic heating system takes longer to heat up than other types of heating systems. | Because the heated water must travel through the whole system, it takes longer to heat a space. |
| A hydronic heating system is not ideal for setting the heat temperature lower at night. | Because a hydronic system takes longer to heat up, it is better to set the thermostat at a consistent temperature. |
| If you use baseboard convectors as part of your hydronic system, you need extra space around the convectors. | You will need extra space near convectors and this may interfere with your furniture arrangement.. |
| A hydronic system’s tank might require regular maintenance. | The tanks/boilers should be drained often to maintain optimum, operation. |
| If your hydronic system encounters problems it might be difficult to get access to the tubing. | The tubing of the system is concealed in the floor or the walls. This makes repairs difficult. |
| It is more expensive to install a hydronic system than any other heating system. | The operating costs are lower than other systems’ costs but the materials and labor for hydronic installation are higher. |
| If you have a hydronic heating system, you most probably need a separate air conditioner to cool down your home in the summer. | Although a hydronic system can also cool down your home, it is not so successful on very warm days. Thus, a separate cooling system is often needed. |
| Water could potentially freeze in sections of your hydronic system during a power outage. | The components of your hydronic heating system could be damaged if exposed to freezing temperatures and no heated water is supplied when the pump is down as a result of a power outage. |
| A hydronic heating system requires careful planning before installation. | The incorrect placing of the hydronic heating system’s pump and unplanned tubing layout can cause you serious problems and will not give you top-performance heating. |
| The air inside your home might become stagnant if you use a hydronic heating system. | Since air isn’t circulating when you use a hydronic heating system, you might experience a lack of ventilation which can cause the inside air to get stagnant. |
| You can’t install a hydronic heating system over an existing floor. | To install a floor hydronic system in an existing house, you have to remove the floor for the tubing to be placed. |
| It is expensive to add a hydronic system to an old house. | When you want to install a hydronic heating system to service your whole old house it can be very costly because all the surfaces where you want the system to operate have to be opened up to place the tubing. |
6. Things that Can Go Wrong with a Radiant Flooring Installation during the house-building process
Without good planning, things can go terribly wrong with the installation of your radiant flooring installation when a new house is being built for you. Most of the problems originate as a result of bad communication between the different trades involved in building your house and installing the hydronic heating system.
There should be good communication between all the trades involved, like the foundation-laying crews, insulation installers, flooring installers, and the hydronic heating system installers as they all have some connection with the installation of the system.
There are many different steps that go into building a home and each of the house’s systems needs to work together to provide a safe, comfortable environment for your family.
6.1 Things being done incorrectly by other workers than the heating system installers
The most common problems that occur are the following:
6.1.1 No Insulation between the foundation and the soil
It is very important that the foundation of your house is very well insulated from the soil. The reason for this is to be found in what is called the wet installation of radiant flooring. This means that the hydronic heating tubing is set into wet concrete. When the concrete that is forming the foundation of the building is dry, the concrete itself radiates heat into the home. If there is no or insufficient insulation between the foundation and the soil the heat goes into the soil instead of into the house.
6.1.2 No Heat Reflectors or proper insulation
With the newest radiant flooring technology, it is possible to add hydronic heating above floor joists. This allows you to install radiant heating also on second floors and above basements.
This means that on the ground floor of your home you can have radiant heat in the floors and ceiling. Good insulation and heat reflectors are needed to keep the heated areas separated. This is normally done with heat reflectors. The reflectors direct the heat to the right rooms on the right floors.
The architect, builders, and craftsmen have to know that you intend to use radiant heating on the second floor as well so that they can fit the right insulations.
6.1.3 Accidental damage
If the workers in all the trades are not informed that there are heating system tubings in the floors and/or walls, they can accidentally damage the tubing when for instance drilling a hole or installing a cupboard in a room.
6.1.4 Incorrect flooring
Although you can nowadays literary use any flooring with your radiant heating systems, certain types of flooring can lessen the heating effect. Some carpets can cause a problem. Therefore the flooring company must know that you plan to have floor radiant heating so that they can consult with the heating company to advise you on the correct type of carpet to choose.
6.2 The things that can go wrong as a result of incorrect installation
The installers of your hydronic heating system can also make mistakes during the installation process. There is a smaller chance for mistakes to slip in if you use installers who are insured, qualified, and certified to install hydronic heated floors. Also, ensure that they offer a solid warranty.
The problems that might occur as a result of bad installation include the following
6.2.1 Water leaks
Poorly done tubing connections are mostly the reason for water leaks to develop. Unfortunately, leaks can’t be detected until the system, and thus the tubing is pressurized.
6.2.2 Freezing
Freezing of water can occur if the heating system, or part of the system, has been installed but the construction of the house is not complete. Water left in the already installed tubing after initial testing can then easily freeze during cold nights.
This is the reason why reputable heat installers test the system at several stages during the construction period. They will also ensure that no water is left in the tubing before the construction is completed. If needed, the installers will add antifreeze to prevent a freezing possibility.
6.2.3 Air in the System
Hydronic heating systems work silently unless there is air in the tubes. The air can cause the system to get noisy. And oxygen in a closed system can corrode the plumbing connections and even damage the pump and seals. Oxygen also produces scale in the water. When the scale builds up it can over time create blockages in the tubes.
The installers of your heating system have to test the closed system for air before and after the house is completed. If no air checking has been done and the air removed, you will encounter problems later on.
6.3 Tip for when you’ve moved into your new home
After you have moved into your home you have to remember to inform anyone who works on the house in the future that you have a hydronic heating system in the floors and/or walls of your home. If possible, it will be good to have the tubing diagram the heating installation company has used.
7. How to install a hydronic heating system beneath the floors of your home
There are various ways how a hydronic heating system can be installed in your home. It depends on whether it has to be installed while constructing a new house, be added to an older already installed system, or be fully installed in an older house.
But although there are many different ways to install a residential hydronic heating system, there are a few most common ways of installing. We’ll have a look at these most common installation methods
Radiant floors can be installed with a “wet” or “dry” installation method. Whichever method is used to install your system, insulation has to be placed to ensure the heat is directed into the home and not away.
7.1 Wet installation
When a wet installation is done, they, in principle, place the radiant tubing into a bed of concrete. This is usually a very effective way of installing the system because the concrete protects the tubing and simultaneously provides a thermal mass to absorb the heat and radiate it evenly throughout the room.
There are two different types of wet installation:
7.1.1 Slab on grade foundations
With this process, the tubing is secured to the reinforcing structure within the slab before the wet concrete is poured into the foundation.
7.1.2 Thin Slab
This method is ideal for when a hydronic heating system is needed on a second floor, but can also be used for ground floor rooms. The installers attach the tubing to the subfloor and then a thin layer of self-leveling concrete is poured over it. Remember, this will raise the floor height and the home structure has to be designed to support the extra weight.
7.2 Dry installation
Dry systems of radiant flooring installation are also called plate systems. With dry installations, the installers use prebuilt panels with tracks for the tubing. The installers place the tubes wherever needed before covering everything with the flooring material.
8. Costs of Hydronic Heating
The upfront costs of a hydronic heating system are usually more than any other heating system. But the good news is that the longer you have your hydronic system, the more cost-effective it is becoming compared to other heating systems.
Generally, the installation of a hydronic radiant floor heating can range from $3 to $7 per square foot, excluding the boiler and pump system’s costs. In total, it costs about three times more to purchase all the parts and install a hydronic heating system than what other heating systems cost.
But the final amount depends on many factors, including the architecture of the house, the installers’ fees in your area, and the installation method.
8.1 You can reduce hydronic heating installation costs
8.1.1 Use the thin slab wet installation method
If the thin slab method of wet installation is used, the costs can be kept lower. With this method, you don’t have to purchase expensive prefab panels. Usually, this method only needs one load of pouring concrete.
8.1.2 DIY
Not many homeowners will be able to install a hydronic heating system the DIY way. You need technical knowledge and know-how to handle all the installation aspects. But if you are skilled you can follow the DIY route and in the process save yourself the money you should have paid for labor.
8.1.3 Utilize the government’s tax incentives
In the United States, there are government tax incentives available for homeowners who install energy-efficient heating systems. The tax breaks can take out a part of the burden of the upfront installation cost.
8.2 Long-term savings with hydronic radiant flooring
As a homeowner, you can typically save between 20% to 40% with a hydronic radiant heating system, as compared to the traditional forced-air systems. Thus, if you foresee staying in the house for a long time, the high initial costs will be canceled out by the low monthly cost, compared with other heating systems.
9. Hydronic Heating Vs Forced-Air Heating
Earlier in this article, we discussed the cost and efficiency aspects and indicated that when you look at the initial purchase price and installation fees only, a hydronic heating system is more expensive than other heating systems. But when you look at the monthly running costs the hydronic heating system is much more cost-efficient than any other heating method.
But let’s compare the comfort and health aspects as well.
9.1 Comfort
- Overall hydronic heating offers more comfort than forced air.
- Forced air has the ability to quickly raise temperatures. Hydronic heating is slower with temperature changes.
- Hydronic heating heats the entire room evenly and simultaneously keeps tile floor comfortable to walk upon
- Hydronic heating doesn’t dry out the air.
- Forced air can be loud, while hydronic heat works silently.
9.2 Health
Health-wise, a hydronic heating system is much healthier than a forced-air system. Even with all the sophisticated filters used by forced-air systems, they are still a problem for people who are highly allergic or suffer asthma problems.
As a hydronic system doesn’t blow any air into a room any person suffering from asthma, other lung problems, or allergies will be much more comfortable in a room heated by hydronic heating than a forced-air heated room.
FAQs
Does hydronic heating use a lot of water?
A: Although a hydronic heating system uses water to provide heat, the water is constantly recycled. The system doesn’t need any more water than the water that has originally been put into the system apart from a small amount of water to top up the system during its yearly service.
How long does a hydronic heating system last?
A: Typically, a hydronic heating system functions efficiently for anywhere between 10 to 20 years.
Can radiant heating be used for cooling?
A: Yes it can. Just as water is effective at conducting heat, so too can it effectively convey cooling when cold water is flowing through the tubing.
Conclusion
Although hydronic heating is initially more expensive than other types of heating systems to install, it is such an energy and cost-efficient system that in the long-term no other heating system can compare with it. Furthermore, it is environmentally friendly and usually doesn’t need maintenance apart from a yearly top-up of the water in the system. I recommend that you seriously consider installing a hydronic heating system in your new home.
